
Prematurity is the leading cause of death in children under five; each year, approximately 15 million babies are born prematurely all over the world. Prematurity exposes the child and the mother to an increased risk of morbidity and death when the caregivers are not trained in specific care. The research team has developed 2 innovative training modules for training in obstetrical emergencies. The first module is a uterine cervix module created to simulate different configurations of cervical effacement. This automated training tool will allow the simulation of emergency or daily clinical situations related to pregnancy, in particular the threat of premature delivery. The second module is a 3D printed “uterine body”. The training module reproduces different scenarios to treat hemorrhages during childbirth (suture, intrauterine tamponade balloon) in order to improve professional practices and reduce maternal morbidity and mortality.

Multi-image fusion is a good solution for performing super-resolution and denoising images, especially for low-cost image capture systems. However, in embedded systems such as satellites, drones or smartphones, the lightweight embedded processing can be problematic. The innovative process optimizes the distribution of the computational load between the light-embedded processing device and the remote processing solution with a more powerful server. It can also considerably reduce the quantity of data to be transmitted or increase the quality of the result obtained for an equal quantity of data transmitted.

Assessing DNA integrity is a crucial step to characterize the quality of biological samples prior to in-depth genomic analysis, especially applicable in reproductive medicine, prenatal diagnosis and cancer research. Although many methods have been proposed for the assessment of DNA integrity (by electrophoresis, quantitative PCR and, more recently, microfluidic-based procedures), there is still a need to apply more sensitive and precise methods. The invention relates to a method for determining the level of integrity of DNA molecules in a sample containing DNA by multiplexing Digital PCR, which involves amplifying DNA fragments from the sample with amplification primers designed to produce different and predetermined sizes of overlapping amplicons of the same DNA target region, and oligonucleotide probes which can produce detectable and differential signals upon hybridization. Proof of concepts in two main applications have been carried out to date on human clinical samples (small cohort studies):
- By evaluating the ability of the developed clinical trial to discriminate plasma DNA samples from healthy subjects (n=25) and cancer patients (colorectal cancer (n=23), gastric cancer (n=22), pancreatic cancer (n=11))
- By evaluating the quality of DNA after storage in different blood collection tubes
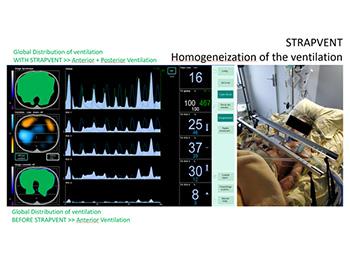
Lung injury is not homogeneous because lesions are frequently distributed in the posterior regions. This exposes the lungs to inhomogeneous ventilation under mechanical ventilation with risk of overdistension of the anterior and
cyclic opening-closing of the posterior regions. These two phenomena can aggravate lung damage and lead to excess mortality. Today, no technical solution allows the homogenization of the pulmonary aeration except the prone position. The research team develops «STRAPVENT», a device whose objective is to apply a titrated compression on the compliant anterior chest wall of the thorax. This device allows a more homogeneous distribution of ventilation, protecting the anterior areas from overdistension and favoring the redistribution of ventilation towards the posterior regions. Dramatic improvement in the airways mechanics has been reported in patients with ARDS.
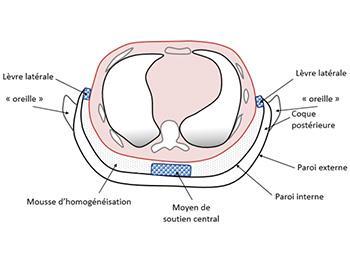
60% of patients admitted to intensive care are ventilated by mechanical ventilation to ensure stability and survival. These patients suffer from lesions induced by various pathologies. Lesions located in the alveoli are not evenly distributed, especially in the less compliant posterior lobes. Today, no technical solution allows a re-homogenization of this ventilation. The research team develops «VacuoVent», a device in the form of a bespoke rigid or semi-rigid thoracic shell allowing the application of an extra-thoracic negative pressure on the thoracic wall in front of the damaged lung. This device allows a more homogeneous distribution of ventilation, and is currently being evaluated on cadavers. Next step: the clinical POC.
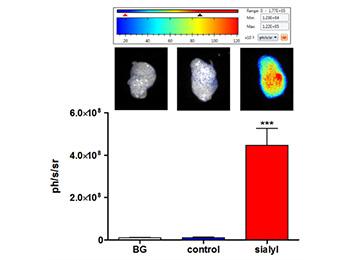
While surgery is the main line of treatment for most solid tumors, incomplete tumor resection frequently occurs and represents an additional risk for relapse. The main challenge for surgeons is then to distinguish the surgical boundary between the lesion and the surrounding healthy tissues in an accurate manner. The research team has developed a new specific imaging agent emitting in the tissue transparency zone and targeting E-selectin, a well-known inflammation marker frequently overexpressed in several solid cancers. The imaging agent is capable to specifically detect colorectal tumor in vivo in a mouse xenograft model. This new agent can be used with portable optical imaging systems in the operating room to delineate tumor areas in order to assist surgeons in real time during resection.
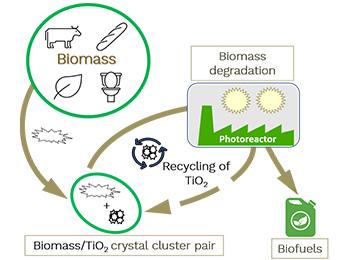
A new biomass conversion process producing biofuels at low temperature. Titanium dioxide crystal clusters are combined with green wastes in water creating a photo catalyst-feedstock pair. The total degradation of the green wastes occurs during exposure to visible light irradiation through TiO2 photo catalysis. After this step, the products are collected and the recovered aqueous TiO2 is combined with new green wastes to form a new feedstock pair, ready for the photocatalytic degradation step. This efficient circular process is a totally solvent-free process.
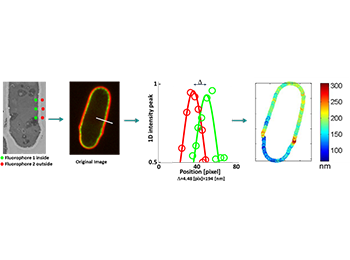
Fungal diseases are highly relevant to human health and agriculture.
In Humans, Candidiasis, Aspergillosis or Cryptococcosis mostly affect immunocompromised patients and cause death penalties of ~1.7 million deaths per year. In plants, fungal diseases cause around 10-30% loss in crops representing a risk for food availability. While anti-fungal treatments remain unsatisfactory to date due to species diversity and adaptation mechanisms, we need new tools to assess the efficiency of newly developed drugs. Cell wall thickness is critical for the survival and development of fungal cells.
The team has developed a new method based on light microscopy and image analysis pipelines to monitor Cell Wall thickness in live cells and in large populations of living cells, thereby allowing to quickly and accurately define the thickness of the cell wall. This method can be used in fundamental and applied research, and is compatible with screening strategies to allow the identification of new agents capable of altering the cell wall.
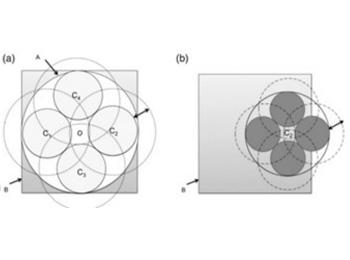
New optimization algorithm based on fractal decomposition. Thanks to a new approach of covering space this algorithm can solve problems with a large number of variables while providing an exact answer. All this with a very low complexity (logarithmic).
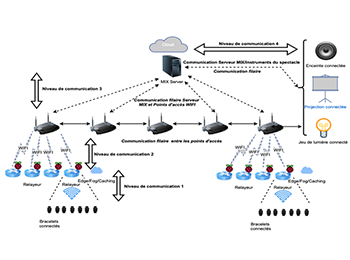
The use of a large number of connected objects in a small area causes problems at the level of the IoT network: on the one hand, an increase in delays (high contention to access the channel) and on the other hand a congestion and high packet loss rate, due to the large volume of data generated. This is the case, for example, of the connected bracelets used by spectators, gathered in restricted areas (concert halls, stadiums, etc.), to produce light effects synchronously via remote control. The proposed solution based on a multi-tier mesh network architecture with four levels of communication and algorithms makes it possible to overcome this problem and ensure an adequate quality of service (QoS).

Viologen derivatives have the ability to change color in UV-Vis range as well as to strongly absorb in near-IR. Their redox properties can also be used for electrochemical energy storage.
Based on these multifunctional materials, we are developing a dual system with electrochromic properties to adjust the optical contrast as well as the ability to store energy, resulting in an electrochromic energy storage system. Unlike commercial systems, transparent mode is here achieved without current, significantly reducing system power consumption. The organic layers can be deposited either on rigid glass or on flexible plastics. Finally, this system is being developed using bio-based products.
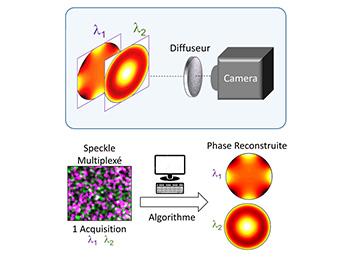
All existing Wavefront sensors (WFS) can only measure several wavefronts by sequential image acquisition. Sequential multi-spectral WFS has several drawbacks: it is difficult to implement, expensive, and incompatible with single-pulse laser characterization. This innovative system now allows simultaneous wavefront shapes measurement at different wavelengths using the multi-spectral (broadband or multi-line) light beam. It relies on the recent development of a wavefront analyzer (DiPSI) based on the use of a simple diffuser that obviates all these drawbacks by performing spectral measurements simultaneously. This aspect is advantageous for a variety of applications such as optical metrology, laser metrology, quantitative phase imaging and ophthalmology.
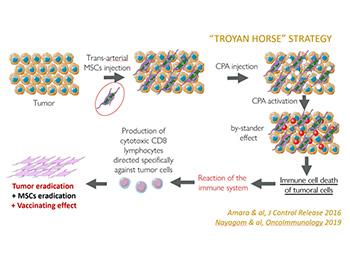
This so called « Gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy (GDEPT) » consists in bringing an optimized gene - allowing to convert cyclophosphamide (CPA) into toxic metabolites 13 times more than native conversion - into the tumors, thanks to an efficient vector, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and a specific (intra-arterial) administration. There, it eradicates the tumor and triggers a specific immune response, resulting in a vaccinating effect. POC in vivo have been established either in mice (treatment and rechallenge experiments), but also in an orthotopic model of hepatocarcinoma (VX2) in rabbits. Those last experiments confirmed breakthrough results, compared to Gold Standard (chemoembolization), either in terms of tumor & metastasis drastic reduction but also remission levels...
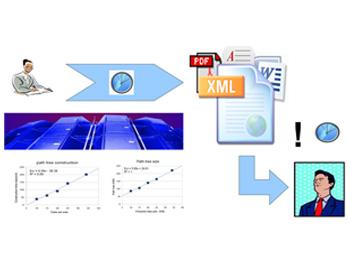
Homomorphic cryptography makes it possible to host encrypted documents in the Cloud, while offering queries on their content, without exposing secret data. However, many Internet applications of document computing require processing massive streams of XML data, which poses real technological challenges for the efficiency of processing techniques and data security. CSQM, the completely new model proposed, is a flow processing approach which makes it possible to minimize the consumption of resources (time, memory) for a given request on a document of any size.
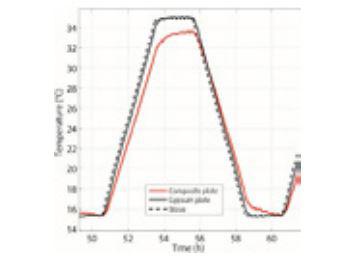
PCM improves thermal performances of materials by delaying temperature increase and decrease and by mitigating the temperature peaks. Most PCM available are based on state change implying solid and liquid transitions which present major issues such as leakage risks and volume variations.
Our technology is based on a solid-solid phase change material that avoids any of these issues. The temperature of phase change can be tuned between 20°C to 65°C according to the application. The PCM presents a Shore hardness which allows its grinding up to grain size lower than 50 μm. The grain size of the PCM can be controlled by sieving for injection in different matrixes (plaster, plastics...). The environmental impact of the PCM is limited, as the synthesis process does not involve any solvent or catalyst.
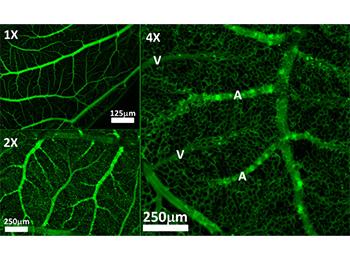

PTL Dx is a panel of new biomarkers of the cervicovaginal secretions predicting spontaneous preterm birth in a 24h window.

Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common lymphoma in adults. Even though cure rates have significantly improved in the last few years since the introduction of new immunochemotherapy treatments, refractory/ relapse cases reach up to 40%. DLBCL is a highly heterogeneous disease and new biomarkers are highly awaited for better DLBCL stratification, prognosis and tailored therapies. We have shown that the transcription factor RelB is frequently activated in a large cohort of DLBCL patients and cell lines independently of their known subtypes, and that RelB activity defines a new subset of DLBCL patients with a peculiar gene expression profile and mutational pattern. Additionally, the newly defined RelB-positive subgroup exhibits a dismal outcome following immunochemotherapy. This new RelB signature then contributes to better DLBCL patient’s stratification and prognosis and paves the way toward new therapeutic approaches based on RelB activation status.
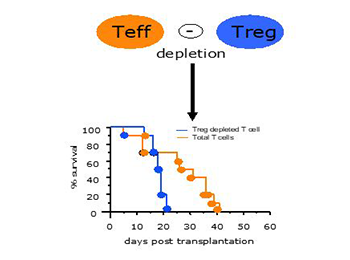
Blood malignancy such as chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and lymphomas are pathologies dealing with a high relapse rate. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Allo-HCT) and Donor lymphocyte injections (DLI) are among potential strategies to treat or prevent relapse, however, response rate generally remains low. Treg cells play a key role in the fine tuning of the immune responses in alloHCT. Cell therapy using Treg infusions to prevent graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) showed very promising results in the clinic. Conversely, ex vivo Treg depletion from DLI has been shown to enhance the graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect in patients who relapsed after alloHCT without previously developing GVHD. Using an anti-TNFR2 mAb, the team provided proof of concept that an anti-TNFR2 treatment can mediate a potent GVL/GVT effect in different experimental models of hematological malignancy relapse after alloSCT through inhibition of Treg population. These results pave the way toward a novel immune checkpoint therapy to modulate alloreactivity after allo-HCT through the TNF/TNFR2 signaling pathway and, more widely, open new perspectives to amplify antitumor responses in solid cancers by directly targeting Tregs and tumor cells through their TNFR2 expression.
Erganeo is at your disposal.